HIPAA-Compliance for Telehealth Video Conferencing
Hayley Spooner, Jun 7, 2023

With telehealth, providers and patients must consider how to maintain the same level of privacy as an in-office visit. Here’s what HIPAA compliance looks like in a telehealth video conference and the best practices for providers to follow.
Highlights:
- HIPAA compliance in a telehealth video conference requires providers to consider their technology, access control, internal processes and data storage.
- Best practices for HIPAA compliance include verifying patient identities prior to beginning consultations and limiting access to the virtual consultation.
- Neat devices support HIPAA-compliant platforms and elevate the telehealth video conference experience without collecting, storing or processing personal health information.
Overview of telehealth video conferencing and HIPAA compliance
Telehealth is a method of delivering healthcare via digital channels, such as video conferencing. Patients use their own device to video chat with a provider in real-time. Providers can write subscriptions, diagnose issues and make recommendations similar to an in-office visit.CDC datashows that 37% of patients have used telehealth in the last 12 months.
Like in-office visits, telehealth video conferences are subject to HIPAA compliance. HIPAA (or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is the federal law that sets the standards for protecting sensitive patient information from being disclosed without the patient’s knowledge or consent. Anyone who handles patient information (providers, nurses, schedulers, insurance companies, etc.) are bound to HIPAA compliance.
The rise of telehealth video conferencing has creatednew questionsabout how to maintain HIPAA compliance. The ease of use that makes telehealth attractive for patients and providers can also make it easy for hackers to access personal health information. This can evolve into medical fraud or identity theft. It’s imperative for providers to use telehealth video conference technology that’s HIPAA-compliant and to understand the risks and challenges that come with teleconferencing.
Ensuring HIPAA compliance in telehealth video conferencing
Technology that can facilitate a telehealth video conference may not always be HIPAA-compliant, creating a risk of patient information being unintentionally disclosed. To ensure patient privacy and improve the future outlook for telehealth, technology decision-makers should consider the following areas to maintain HIPAA compliance.
Technical safeguards
HIPAA standards include technical safeguards to address security challenges and protect patient information. Examples of technical safeguards include access control, storage and disposal, and transmission security.
Access control
In the context of telehealth video conference platforms, technology should allow only authorized users to access and start video consultations. The meeting link should be shared only with the provider and the patient. If the consultation is being recorded, patients must be notified and give their consent to being recorded. Video conferencing software is usually independent of other medical technology like patient charts and patient portals, which require additional credentials.
Neat devices offer the convenience of one-touch meetings while maintaining user security and privacy. Users can log into their individual video conferencing accounts to access one-on-one patient meetings, ensuring no one else has access to the consultation. Headphones can also be paired to the device so that only the provider hears what the patient shares.

Storage and disposal
Cloud-based data storage allows healthcare providers to easily access patient data remotely. However, some telehealth apps and video conferencing platformsmay collect directly from consumersand may not be bound by HIPAA regulations. It’s essential to choose technologies that are HIPAA-compliant and properly store and dispose of data.
Transmission security
Encryption involves encoding data to prevent unauthorized access during transmission or storage. It protects patient data (social security numbers, medical history, diagnoses, treatments, etc.) from cybercriminals who might attempt to intercept or steal it during transmission.
During a telehealth session, data may be shared between the provider and the patient. Video conferencing platforms should support encryption technologies to maintain patient privacy.
Physical safeguards
Physical safeguards include device or workstation use, along with device and media controls. Applied to telehealth video conference platforms, facilities should consider creating dedicated spaces for telehealth consultations. Implementing access control in these spaces and offering permanent technology setups ensure that only authorized providers are meeting with patients. Having the ideal environment for private video consultations also minimizes the risk of patient data being inadvertently shared whileblocking out background noise.
Workstation use & security
Workstations serve as an access point to patient health information. Employees not trained in proper workstation use and security can become a liability. Access controls, automatic log-offs after a period of time, regular software patches and updates, routine audits and antivirus software that employees can’t disable support HIPAA compliance.
Facilities might also consider positioning permanent workstations where non-users cannot view patient information. Keeping an inventory of physical workstation components and tracking mobile workstation movements through the facility helps you better manage your devices. Also, remove access to workstations within 24 hours of an employee’s termination to further prevent unauthorized access.
Device and media controls
Not all devices are good candidates for storing, transmitting or otherwise handling sensitive patient data. Standardizing your devices and media reduces the potential for data misuse. This way, data doesn’t wind up on personal devices or devices that might be vulnerable to security issues or breaches.
Administrative safeguards
Administrative safeguards refer to the“actions, and policies and procedures, to manage the selection, development, implementation, and maintenance of security measures to protect electronic protected health information and to manage the conduct of the covered entity’s workforce in relation to the protection of that information,” according toHHS.gov. These comprise over half of HIPAA security requirements and include security management processes, risk assessments and breach notifications.
Security management processes
Security management processes create a blueprint to maintain HIPAA compliance. These help to train employees on maintaining compliance and protecting patient health information.
Risk assessments
Risk assessments are part of developing security management processes. Identify potential threats to security along with the probability of issues occurring and the impact of those issues if they do occur.
Breach notifications
Having a plan in place to handle breaches if they occur allows organizations to quickly mitigate a breach’s impact. This includes having processes to identify unauthorized access, notifying patients their data may have been compromised, sealing data leaks and improving defenses against future breaches.
Best practices for HIPAA-compliant telehealth video conferencing
Telehealth is still new territory for many healthcare organizations. Following these best practices for HIPAA-compliant telehealth video conferencing can reduce your risk and improve the overall patient experience.
Verification of patient identity
Before diving into the patient’s concerns, make sure you’re speaking with the right patient. Ask them to verify their name, birth date, address or other details so you don’t inadvertently share information with the wrong person.
Limiting access to the virtual consultation
Consultation links should be shared on an as-needed basis. Using encryption software and password-protected meetings ensures that only the provider and the patient can join the conversation.
Providing patient education on HIPAA compliance
Share with patients how you’re protecting their privacy on their telehealth video conference. Provide them with a copy of your procedures and protocols to set the right expectations and build their confidence.
Implementation of security policies and procedures
Put your security blueprint into practice. Make sure employees understand your policies and follow them, and be prepared to hold them accountable when they don’t.
Regular training of staff
Regularly training your staff on HIPAA compliance in the context of telehealth creates opportunities for questions. It also helps staff think critically about how they’re conducting telehealth sessions and identify potential issues or inefficiencies that should be addressed.
Neat + HIPAA compliance
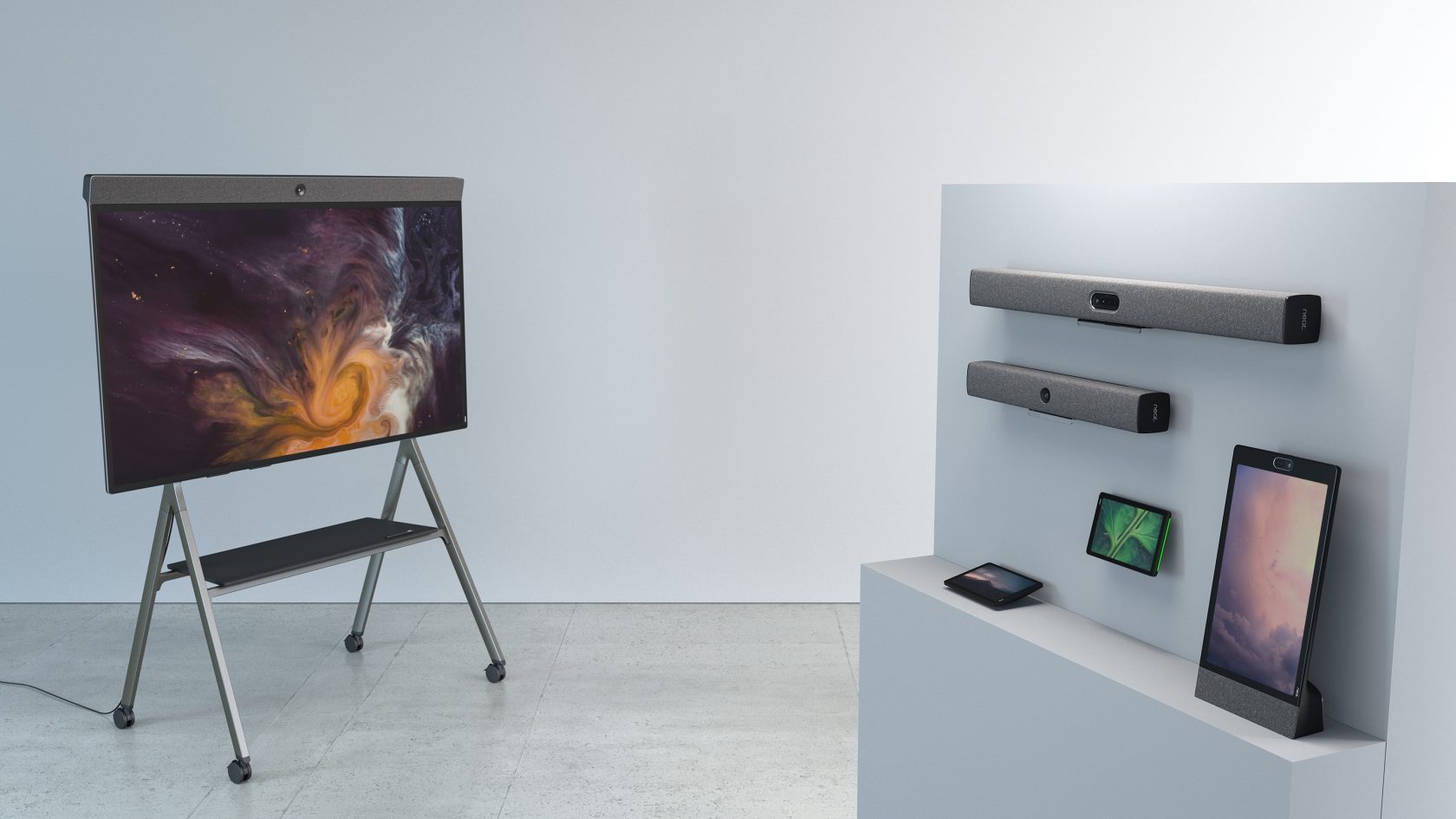
Neat devices support HIPAA-compliant video conferencing platforms likeMicrosoft TeamsandZoom, both of which have been game-changing for telehealth. These platforms offer patients a secure and user-friendly experience, along with the convenience of telehealth.
Connecting with patients on Neat devices gives you crystal-clear audio and video, allowing you to better hear and see patients’ facial expressions and physical areas of concern. Whether you’re checking a mole or a rash or listening to a patient describe their symptoms, Neat enables you to give your professional opinion with confidence. ExploreNeat devicestoday.
FAQs
What is telehealth video conferencing?
Telehealth video conferencing allows patients to consult with their doctor or a medical provider via web-based or mobile apps from the comfort of their homes. This option significantly reduces cost and time compared to traditional in-office visits while also providing greater access to medical consultations.
What is HIPAA compliance?
HIPAA (the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)is a U.S. federal law enacted in 1996 that provides individuals with privacy protections for their health information. It also holds healthcare providers and insurers accountable for protecting sensitive patient data. This gives patients more control over their health information, including who can access it and how it’s shared.
Why is HIPAA compliance important in telehealth video conferencing?
Video conferencing has created new challenges for providers and patients, particularly concerning healthcare data. These challenges include potentially unsecured connections, unauthorized access to patient consultations, access to patient data and the live transmission of data between patients and providers. Any technology used in a telehealth video conference should maintain patient privacy as though they were in the office.
How can I ensure HIPAA compliance in telehealth video conferencing?
Using HIPAA-compliant technologies reduces many of the risks associated with telehealth. Healthcare organizations should also implement processes and procedures to verify patient identities, limit access and secure patient data. While popular platforms like Microsoft Teams and Zoom are generally HIPAA-compliant, know that this compliance isn’t always guaranteed. For example, Teams is HIPAA compliant as long as certain conditions are met, including the customer having a valid Business Associate Agreement (BAA) in place with Microsoft. Understanding the terms and conditions of your technology in the context of HIPAA will help you make informed decisions.
What are the best practices for HIPAA-compliant telehealth video conferencing?
Verify patient identities before moving on to the consultation. Limit access to patient consultations and share the link only with those that are participating in the consultation. Educate patients on HIPAA compliance and how your telehealth services meet HIPAA standards. Implement security protocols and procedures to proactively protect patient data. Most importantly, regularly train your staff on HIPAA compliance and best practices to keep it top of mind, raise questions and identify and address possible inefficiencies or issues.
Sources:
Telemedicine Use Among Adults: United States, 2021. CDC.
Video conferencing for telehealth: a step-by-step guide. Ring Central.
Security Standards: Technical Safeguards. Dept. Health & Human Services.
Guidance on How the HIPAA Rules Permit Covered Health Care Providers and Health Plans to Use Remote Communication Technologies for Audio-Only Telehealth. Dept. Health & Human Services.
Telehealth privacy for patients. U.S. Government.
Data privacy considerations for telehealth consumers amid COVID-19. National Library of Medicine.